Supports automation of hybrid, native and web apps. Open Source and huge community support. Selenium webdriver compatible. Supports multiple test framework. Appium configuration is a bit complex and tricky some times to implement all kind of mobile OS versions. There should be some utility to compare screens of mobile apps. Appium 2.0 beta versions can be installed using the below command: npm install -g appium@next. Appium server can take up several optional arguments. In addition to the server arguments, Appium 2.0 introduces new arguments: -ah to specify a directory to install Appium drivers. Appium server -ah /path/to/install/drivers driver install uiautomator2.
Appium is an automation testing tool that can be used to validate mobile browsers and mobile applications. This tool is widely used in mobile automation testing because it is free and can support both iOS and Android platforms. Mobile apps have become an important element in our lives because they provide us a smart way of doing things like shopping, paying bills, chatting, and booking flights.
Many mobile apps are constantly being developed to solve various real-life problems. Before these apps are commissioned for use, they are tested to validate their usability, quality, and functionality.

This article takes readers through Appium mobile automation testing tool and discusses its key features. It also provides an overview of Appium architecture and explains how it works.
Introduction to mobile automation testing
Mobile automation testing is the use of automation tools to test new mobile applications before they are commissioned for use. This type of testing is done to check whether mobile applications work well across various operating systems and mobile devices.
Automation in testing increases the speed and accuracy of testing. It is an effective way of checking defects in new mobile applications.
This testing performs various aspects of testing such as usability, security, performance, quality, and functionality. It also tests the ability of a new application to interact with other applications.
What is Appium?
Appium is a popular mobile automation testing tool used for testing mobile browsers and mobile applications. It validates the compatibility, usability, and response time of mobile browsers and applications across various mobile devices.
This software has been limited to mobile application testing, with a specific focus on iOS, Firefox OS, and Android applications. Various programming languages are supported in Appium automation testing. These include Python, PHP, Java, and Perl.
Automation tests in Appium can be run on mobile devices, simulators, and emulators.
A simulator is an imitation of the condition and operation of an application. Similarly, an emulator is software or hardware that allows a computer system (host) to run applications designed for another system (guest).
Automation testing in Appium does not depend on the operating system (OS) of a mobile device. This is because its framework can translate the driver commands into Android or iOS commands that do not depend on the type of the OS. Instead, these commands depend on the type of mobile device.
The following are some of the main types of mobile apps that can be tested using Appium automation testing:
- Native apps: These are platform-specific apps that are developed and operated in Android, iOS, or Windows SDKs. These apps do not have features for web browser navigation.
- Hybrid apps: These are apps that can work well on a certain platform and still have features for web browser navigation. These are mobile applications containing features for web browser navigation.
- Web apps: These are apps that can be accessed using browsers (built-in) of mobile devices.
Prerequisites for using Appium
To use Appium, you need the following prerequisites:
- Node.js
- Java
- Android Studio
- Eclipse IDE
- Appium Server
- Appium Client Library
- Selenium Jar
Why is Appium widely used?
Appium is widely used because of its unique features and the certain benefits it offers mobile app developers. The main features that make developers choose Appium over other mobile automation testing tools are:
- Open source: This tool is open source, which reduces the overall cost of developing and rolling out a mobile application for deployment.
- Cross-platform: Automation testing in Appium can be done on various platforms such as Windows, iOS, and Android. Other tools like Robotium and Selendroid support testing on only Android.
- Multiple mobile apps: Appium allows testing in various types of mobile applications (native, web, and hybrid apps).
- Multiple programming languages: Various programming languages are supported in Appium automation testing. These include Ruby, Javascript, C#, Python, and Java. This gives testers and developers some flexibility on the choice of language.
- Integration: This tool can be used with other external applications such as Selenium Grid and Selenium WebDriver.
- Low memory consumption: The architecture of Appium functions as a proxy between the tool-kit for automation and the test machine.
Appium is also chosen by testers and developers because it offers the following additional benefits:
- It allows the test scripts to be executed simultaneously.
- It contains a recording tool to record test cases and a playback tool for re-running such records.
- Various elements can be tested simultaneously (i.e. emulators, real devices, and simulators).
- It supports cloud-based testing using testdriod.
- Appium is backed by an active community (Google group) that improves the ease and speed of troubleshooting.
Appium architecture
The following diagram shows the architecture of Appium:
The Appium architecture consists of three main components:
- Appium Client
- Appium Server
- End device
Appium client
This contains the automation code (scripted). This code is written in a specific programming language like Java, Python, Ruby, or Perl. The script contains the configuration details of the application and the mobile device. The scripted code and the configuration details are used to run the applications’ test cases.
Appium server
This is an HTTP server that receives command requests (HTTP requests) from the client component (in JSON format). This server uses a Node.js server. The commands are then executed on mobile devices.
This component should be installed on the computer before scripting the automation code. The Appium server acts as an intermediary between the Appium Client and the end device. It is connected to platforms such as iOS, Android, and Windows.
End device
This refers to an emulator or a mobile device that is connected to the Appium server. The test cases are executed on this device.
How does Appium work?
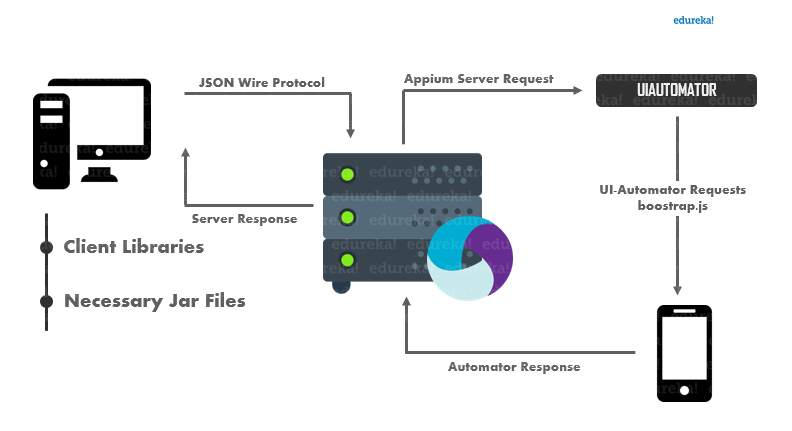
Appium works using the three main components of its architecture (client, server, and end device). When this tool is installed on your computer, it sets up an HTTP server that generates a REST API to enhance communication with the client.
This server collects command requests from the Appium client in JSON format. JSON Wire Protocol is a medium of communication between the server and the client. It plays the role of communicating command requests. These command requests are then executed on the end devices (either on Android, Windows, or iOS).
The Appium server uses a test automation framework to execute requests on the user interface of end devices. For example, it uses the XCUI test to execute commands on iOS. It uses UI Automator to execute command requests on Android platforms (for newer API versions).
Appium Tutorial
The XCUI test allows users to write tests on iOS using Objective-C or Swift. The UI Automator is an Android testing framework that builds user interface (UI) tests using APIs. After the requests have been executed, the Appium server provides HTTP responses to the client.
Appium works differently on iOS and Android. Let’s look at how it works on these two platforms.
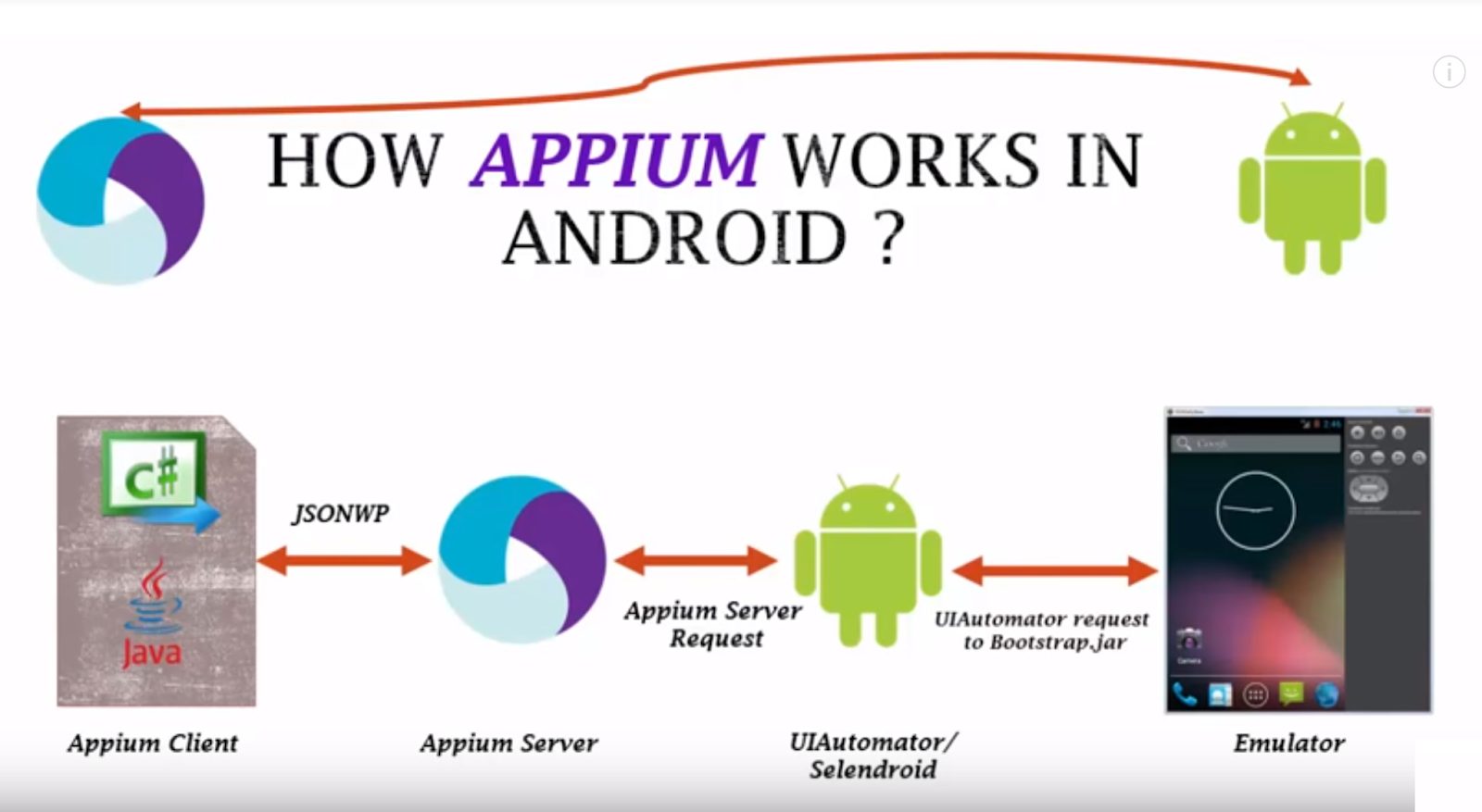
How does Appium work on Android?
The following is a brief sequence of how Appium works on the Android platform:
- The Appium client connects with the HTTP server and uses the JSON Wire Protocol for communication.
- The Appium server receives requests from the client component.
- The server connects with the mobile automation framework for Android (UI Automator or Selendroid).
- Android devices contains bootstrap.jar that receives the test commands from the Appium server. The bootstrap.jar contains executable files that enhance the connection between the server and Android devices. It plays the role of a TCP server since it enhances the secure transmission of test commands to the Android devices.
- The bootstrap.jar uses the UI Automator or Selendroid to execute the command requests on the Android device.
- The test results are then sent to the server, which eventually sends HTTP responses to the Appium client. The HTTP responses contain status codes indicating success or server error.
How does Appium work on iOS?
The following steps show how Appium works on the iOS platform:
- The Appium client connects with the HTTP server and uses the JSON Wire Protocol for communication.
- The Appium server receives requests from the client component.
- The server connects with the mobile automation framework for iOS devices (XCUI test).
- iOS devices contains bootstrap.js that receives the test commands from the Appium server. The bootstrap.js contains executable files that enhance the connection between the server and the iOS devices. It plays the role of a TCP server since it enhances the secure transmission of test commands to the iOS devices.
- The bootstrap.js uses the XCUI test to execute the command requests on iOS device.
- The test results are then sent to the server, that eventually sends HTTP responses to the Appium client. The HTTP responses contain status codes indicating success or server error.
Limitations of Appium
- It is not effective in handling image recognition algorithms. Users may need to employ image handling techniques.
- There is slow execution of test scripts on iOS platforms.
- Appium does not support older Android APIs. Alternatively, Selendroid could be used.
- Using Appium for automation testing requires the installation of other programs. For example, if you want to run test cases in Java, you will need to install Java (JDK), Appium Client Library, Selenium jar, Android SDK, and Eclipse IDE.

Conclusion

Appium Tutorial
In this article, we have learned about mobile automation testing with Appium.
To summarize:
- We gained a basic understanding of mobile automation testing.
- We learned about Appium software and why it is widely used in automation testing.
- We got an overview of Appium architecture.
- We learned how Appium works on Android and iOS.
- We also learned some of the limitations of Appium.
Resources
Peer Review Contributions by: Srishilesh P S
About the author
Onesmus MbaabuAppium.io
Onesmus Mbaabu is a Ph.D. candidate pursuing a doctoral degree in Management Science and Engineering at the School of Management and Economics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), Sichuan Province, China. His interests include economics, data science, emerging technologies, and information systems. His hobbies are playing basketball and listening to music.